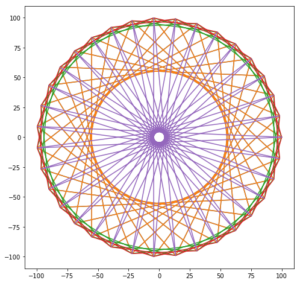
1.母ピンの本数
2.角度
3.リストの素数
によって曼荼羅模様が変わるプログラム
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 |
%matplotlib inline import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import math n = 35#母ピンの本数 kaku = 360 / n #角度 x = [] #ピンの位皿 y = [] #ピンの位皿 pnum = [11,81,101, 3, 17 ] # (1)素数のリスト #索数番目のピンに糸をかける plt.figure(figsize=(8, 8)) for p in pnum: for i in range(n+1): th = math.radians(kaku*i*p) x.append(100 * math.cos(th)) y.append(100 * math.sin(th)) plt.plot(x,y)#模様を壁画 x.clear() # をクリア y.clear() # plt. show() |