階層的クラスタリング、デンドログラフという階層を持つ
非階層的クラスタリングも、階層的クラスタリングと同じように
データから似た性質の法則を探し出し、クラスターを作るが階層構造を持たない。
非階層的クラスタリングはクラスターの数を開発者が決める
大量のデータを扱うのにてきしており、k-means法が使われる
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 |
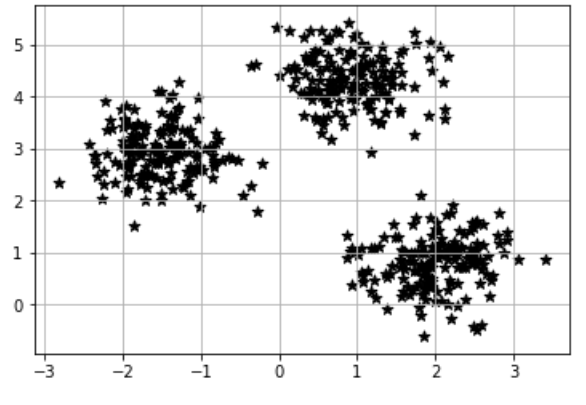
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np import pandas as pd from sklearn.datasets import make_blobs # Xには1つのプロットの(x,y)が、yにはそのプロットの所属するクラスター番号が入る X,y = make_blobs(n_samples=500, # サンプル点の合計 n_features=2, # 特徴量の指定 次元数とも呼ぶ centers=3, # クラスタの個数 cluster_std=0.5, # クラスタ内の標準偏差 shuffle=True, # シャッフル random_state=0) # 乱数生成器を指定 plt.scatter(X[:,0], X[:,1], c='red', marker='*', s=50) #下のサンプルはblack plt.grid() plt.show() |